Today, the ability to transfer funds across international borders is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Still, despite significant technological advancements in the financial sector, cross-border payments continue to present challenges that impact transaction speed, cost, and security.
As a result, the need for efficient cross-border payment mechanisms has never been greater. However, the current infrastructure supporting these transactions often falls short of modern expectations for swiftness, transparency, and cost-effectiveness.
This article explores the five most significant obstacles in international payment processing and provides actionable strategies to overcome them. Our goal is to make stakeholders better equipped to make informed decisions about their international payment strategies. Everyone involved in international transactions must understand these obstacles and the available remedies. Let’s dive in!
1. Regulatory complexity and compliance challenges
The international payment ecosystem operates within a complex web of regulations that vary significantly across jurisdictions. Financial institutions facilitating cross-border transactions must navigate this intricate regulatory landscape while ensuring full compliance with multiple sets of rules simultaneously.
Each country maintains its own regulatory framework governing financial transactions. This creates a patchwork of requirements that payment service providers must satisfy. These regulations encompass everything from customer identification protocols to transaction reporting requirements.The lack of harmonization between these frameworks causes significant complexity in the cross-border payment processing.
In addition, financial institutions must conduct thorough Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) checks on cross-border transactions. These processes are essential for the integrity of the global financial system but often introduce delays in payment processing.
The transmission of personal and financial data across borders raises serious privacy concerns. It also triggers the application of various data protection regulations. Financial institutions must ensure their cross-border payments comply with fundamental industry regulations. These include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S.
How to tackles regulatory complexity and compliance challenges
Invest in regulatory technology (RegTech)
Regulatory technology solutions can automate compliance processes and reduce the manual workload.These systems monitor regulatory changes across multiple jurisdictions and update compliance procedures.
Establish collaborative compliance networks
Financial institutions can form collaborative networks to share compliance resources and intelligence. In this way they will distribute the burden of regulatory monitoring and implementation across multiple organizations. These networks can also facilitate standardized approaches to common compliance challenges.
Engage with regulatory sandboxes
Many regulatory authorities now offer “sandbox” environments. There, financial institutions can test innovative payment solutions under regulatory supervision but with compliance relaxed requirements. These programs help institutions develop compliant solutions while maintaining a dialogue with regulators.
2. Currency conversion and exchange rate volatility
Currency conversion represents a significant challenge in cross-border payments. It introduces both cost and risk factors that can impact the final value received by payment beneficiaries. The exchange rates applied to cross-border transactions often lack transparency.
This makes it difficult for payment senders to understand the true cost of their transactions.
Additionally, the exchange rate quoted at the time of payment initiation may differ from the rate ultimately applied when the transaction is processed. For international businesses, these fluctuations can erode profit margins and complicate financial planning.
Financial institutions must maintain liquidity in multiple currencies to process transactions. This presents significant challenges for smaller institutions with limited resources. Institutions must balance the need for immediate payment processing against the costs of holding funds in various currencies.
Source: digipay.guru
How to tackle currency conversion and exchange rate volatility?
Pre-agreed exchange rates
Payment service providers can offer guaranteed exchange rates that remain valid for a specified period. This will provide certainty to payment senders about the amount that will be received by beneficiaries. The approach shifts the exchange rate risk from customers to the service provider who can then manage this risk.
Multi-currency accounts
Businesses and individuals can maintain accounts in multiple currencies. This will minimize currency conversion for certain payment flows. The accounts allow users to receive funds in one currency and make payments in the same currency with no conversion costs.
Blockchain-based solutions
Distributed ledger technologies offer a possible solution to currency conversion challenges. Some blockchain platforms facilitate near-instantaneous conversion between different currencies, including digital currencies. This reduces the time during which exchange rate fluctuations can impact transaction values.
3. Settlement time and processing delays
The time required to complete cross-border payments is one of the most significant pain points for users. Transactions often take several days to reach their destinations. There are always multiple financial institutions in the payment chain and this contributes to delays, especially when institutions operate in different time zones. Each bank must perform its own compliance checks and reconciliation.
Additionally, any missing or incorrect data can cause further delays. When information such as the recipient’s full name, and bank account details is incomplete or contains errors, manual intervention becomes necessary. The problem is compounded by differing data format requirements across different countries and financial institutions. This all extends processing times.
Many cross-border payments still rely on legacy infrastructure and processes that were not designed for the speed and volume demands of modern global commerce. These systems often operate on batch processing schedules rather than real-time processing. Many legacy systems have limited operating hours and do not function during weekends or holidays.
How to tackle currency conversion and exchange rate volatility?
Real-time payment networks
New payment networks designed specifically for cross-border transactions are emerging to offer near-instantaneous settlement. These networks often bypass the traditional correspondent banking system and reduce the number of intermediaries.
Payment pre-validation
Advanced payment systems can validate recipient information before a transaction is initiated. This pre-validation process can verify that account numbers are in the correct format, that the recipient bank is accessible through the chosen payment route, and that all required regulatory information is present.
ISO 20022 message standards
The adoption of ISO 20022 for financial communications enables richer, more structured data to accompany payment instructions. This standardization reduces the likelihood of information gaps or misinterpretations that could cause processing delays. The enhanced data capacity also supports more efficient compliance processes.
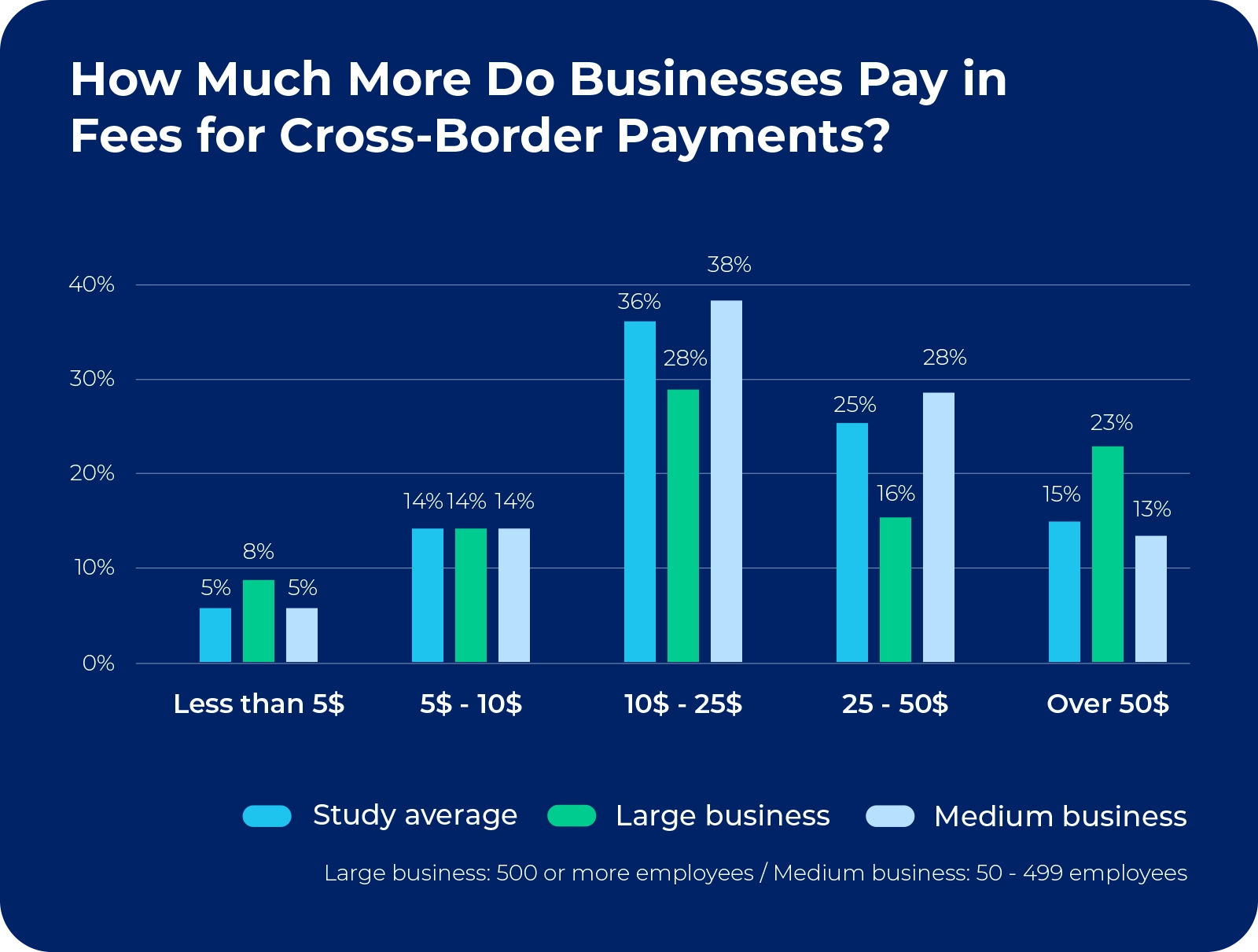
4. Cost inefficiencies and fee structures
Each of the financial institutions involved in the cross-border payments process charges fees. They accumulate and often result in unexpected deductions from the final amount received by the beneficiary. The lack of transparency makes it difficult for payment senders to predict the total cost of their transactions.
Financial institutions often earn revenue from exchange rate margins on cross-border transactions and they can exceed the stated fees. This is especially true for less commonly traded currency pairs. In high-value transactions, small rate differences can mean significant costs.
Correspondent banking relationships are costly to maintain. That is why financial institutions pass these costs on to customers through higher transaction fees. Some institutions terminate relationships in certain regions because of the regulatory burden. This further increases costs for remaining service providers.
Source: rapyd.net
How to tackle cost inefficiencies and fee structures?
Fintech innovations
New financial technology companies are challenging traditional banking models with more cost-effective approaches. These companies often leverage digital platforms, direct currency exchange markets, and more efficient operational models to offer lower fees.
Payment aggregation
To reduce the pre-transaction cost, financial institutions can batch payments by destination. This approach is particularly effective for small-value payments that would otherwise incur disproportionately high fees.
Transparent fee structures
Payment service providers that offer clear, upfront pricing are gaining market share. These providers typically charge a transparent fee and apply exchange rates with minimal margins. They allow customers to understand the true cost of their transactions before they are initiated.
Source: digipay.guru
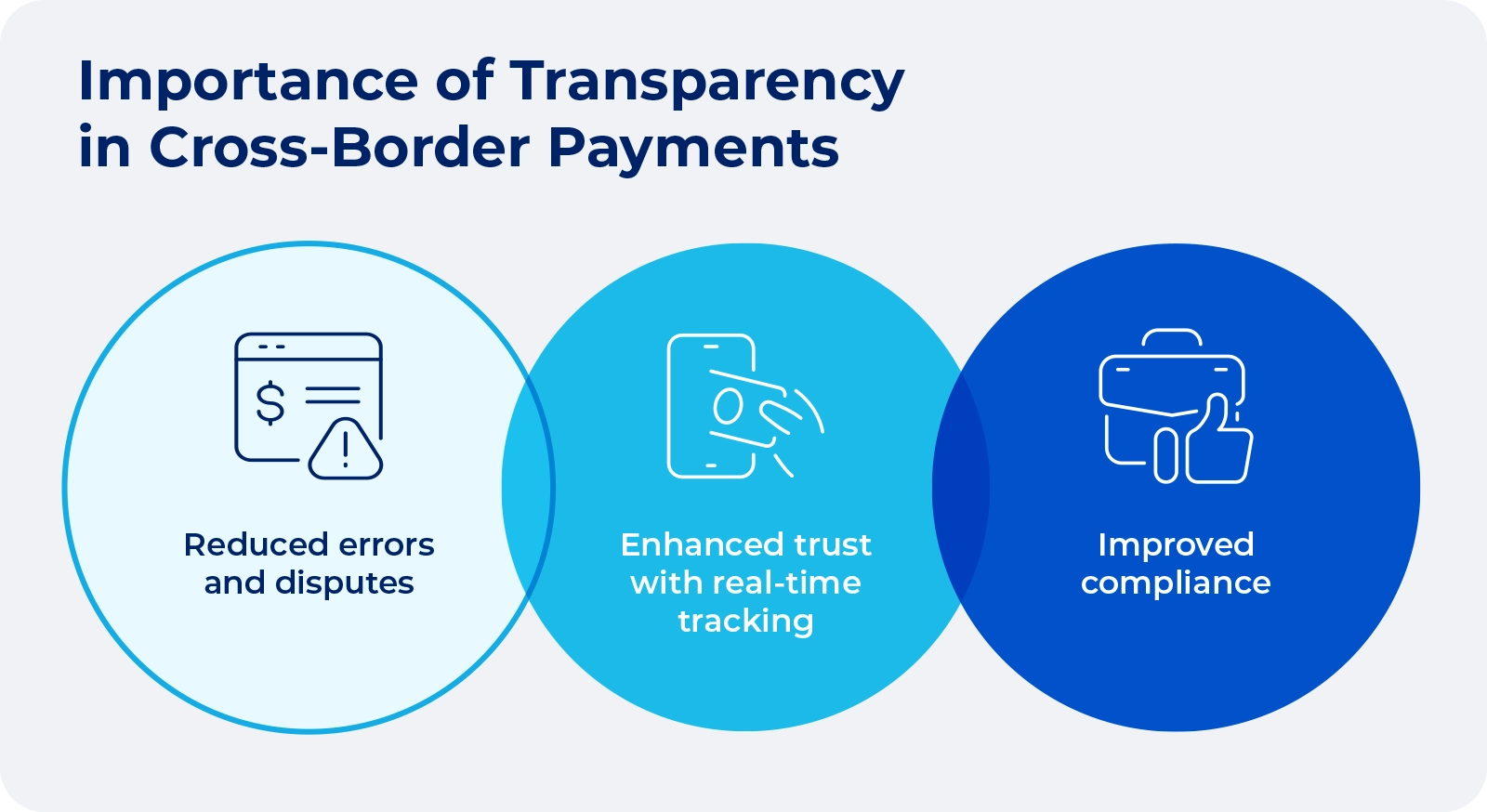
5. Limited transparency and tracking capabilities
Transaction information is often fragmented without complete visibility into the payment journey. This makes it difficult to track payments and to identify the source of any delays or problems that arise. The information gap can create significant anxiety, particularly for time-sensitive or high-value transactions.
If a payment has been delayed, for example, customers might not even get an explanation or an estimated resolution time. This prevents people from taking alternative actions that might address the underlying issue. The information gap can have significant operational implications, especially for businesses.
How to tackle cost inefficiencies and fee structures?
Payment tracking platforms
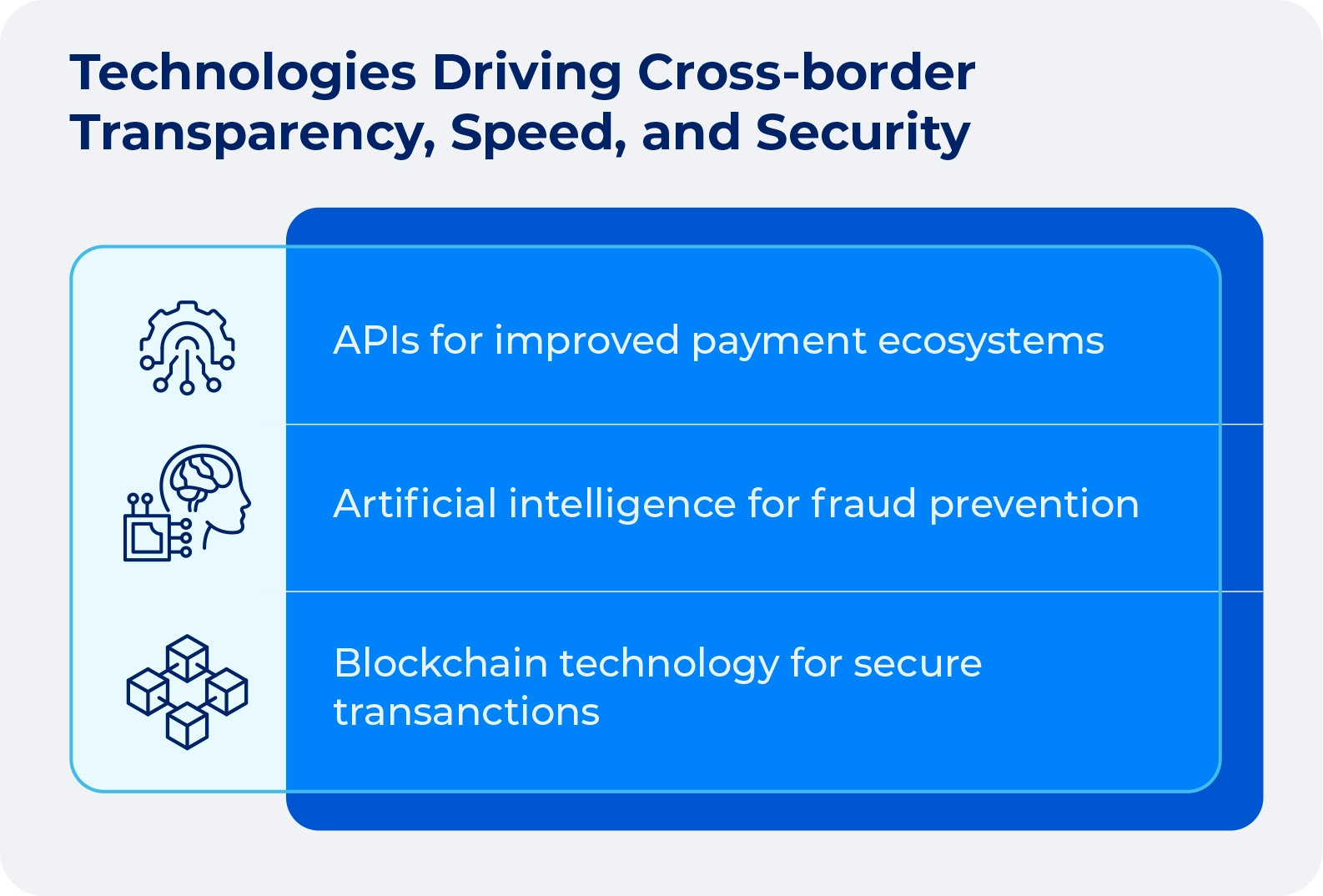
Initiatives like SWIFT’s Global Payments Innovation (GPI) are introducing end-to-end tracking capabilities. These platforms provide real-time visibility into transactions. Users receive confirmation when funds are credited to the recipient. The standardized tracking information is accessible to both sending and receiving banks.
API-Based status notifications
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable real-time communication of payment status information. The interfaces can deliver automated notifications (mobile applications, email, text messages) at each stage of the payment journey. This keeps customers informed without the need to seek updates.
Standardized status definitions
Industry initiatives to standardize the terminology used for payment status updates are improving clarity and consistency in transaction tracking. These standardized definitions ensure that status information means the same thing regardless of which financial institution is providing it.
Summary
Cross-border payments are finally catching up to the pace of global business—but not without a fight. Behind the scenes, outdated systems, regulatory puzzles, and hidden costs still trip things up. The good news? Smarter tech, clearer data, and more pressure from users are starting to crack the code.
It’s simply not enough to make payments faster or cheaper anymore. Cross-border payments must work for people, not just banks. We need a transparent process that’s simple and reliable. The real change will come when global payments stop feeling like a headache and start flowing as easily as sending a quick message.



