Today, effortless international fund transfers are crucial. As economies become more interconnected, the need for cost-effective and transparent payment methods continues to grow.
![Uncover Cross-Border Payments [Complete Guide for 2025]](https://www.scalefocus.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/SF_Cross-border_payments_hero.webp)
This is where cross-border payments come in. They are the lifeblood of international trade and personal financial transactions. We created this comprehensive guide to provide a better understanding of their role.
In it, we explore the significance of cross-border payments in the global economy. We also highlight how digital payments, international eCommerce, and financial globalization have increased their demand.
Most importantly, however, we look into the mechanisms behind cross-border transactions, the challenges they present, and the innovations shaping their future. Our goal is to offer insights into this evolving landscape and help you navigate it successfully.
What are cross-border payments?
When the payer and recipient of a financial transaction are located in different countries, they take part in cross-border payments. These can be large corporate transactions or individual money transfers. They form the backbone of global economic activity—think trade, investment and personal remittances.
Domestic payment systems do not have direct links to those in other countries. Because of this, when a transfer happens between two jurisdictions, the currency does not move physically across borders.
International banks offer accounts to foreign counterparts and hold their own accounts with them. This allows banks to make payments in foreign currency but the funds are not transferred across borders. Instead, accounts are credited in one location and debited in the other. FinTechs and money transfer agents use this network to offer services to both businesses and individual users.
However, not all banks have direct relationships with each other, and they need to use an intermediary bank, known as a correspondent bank. This third bank holds accounts for the other two when they cannot deal directly with one another. This process is called correspondent banking and plays a key role in the global payment system for cross-border transactions.
The more intermediaries involved in a cross-border transaction, the slower and more expensive it becomes. For currency pairs with high payment volumes, like US dollars to British pounds, the process is usually quicker with fewer intermediaries. The more correspondent banks are involved, the longer the transaction takes and the higher the costs at each step.
Types of cross-border payments
1. Wholesale cross-border payments
Wholesale cross-border payments usually occur between financial institutions. They help these institutions handle their customers’ transactions or manage their own activities like borrowing, lending, currency exchange, and trading in assets like stocks, bonds, and commodities.
Governments and large non-financial companies also make use of these payments for big transactions, such as importing, exporting, or trading in financial markets.
2. Retail cross-border payments
These payments usually happen between an individual and a business, yet they include sub-sets. The main ones are person-to-person, person-to-business, and business-to-business. This category also encompasses remittances, which are the money migrants send to their home countries.
Why are cross-border payments important in 2025?
At the start of 2025, the World Economic Forum called cross-border payments an engine for economic growth. They allow people to make transactions when traveling, purchase from international merchants, or send money to family abroad securely and reliably.
One of the main reasons for the rise of cross-border payments in recent years is international trade. The underlying factors also include globalization, global supply chains and the emergence of cross-border marketplaces (Amazon, eBay, Alibaba).
For merchants, these payments offer a more personalized customer experience by allowing them to offer popular regional payment methods. In this way, they can tap into the fast-growing global B2C eCommerce market, which is expected to reach $4,195.4 billion by 2027.
Businesses rely on fast and secure international transactions to expand into new markets and in 2025, cross-border payments will be more important than ever because of increasing globalization, digital commerce, and migration.
How cross-border payments work
For decades, the correspondent banking model has been the cornerstone of cross-border payments. This system operates on the principle of banks maintaining accounts with each other across different countries. Here’s the step-by-step payment flow:
Initiation
When a sender initiates a transfer between different jurisdictions, a cross-border payment process begins. The sender submits a request through a bank, FinTch service, or payment provider along with the recipient’s details and a currency for the transaction. The system then verifies the sender’s identity and checks compliance with financial regulations. Once the request is approved, the payment is ready for processing.
Processing
The payment moves through banks or networks that handle currency conversion and security checks. These intermediaries ensure that the transfer follows legal rules. The sender’s account is debited, and the recipient’s bank prepares to receive the funds. The time this step takes depends on the payment method and the institutions involved.
Settlement & reconciliation
At this stage, the recipient’s bank confirms the payment and deposits the funds into the recipient’s account. It may apply fees or adjust the amount based on exchange rates. Once the funds are available, the transaction is considered complete. There are instances when delays occur when banks have different regulatory processes or need additional security checks. These delays can affect how quickly the recipient gains access to the funds.
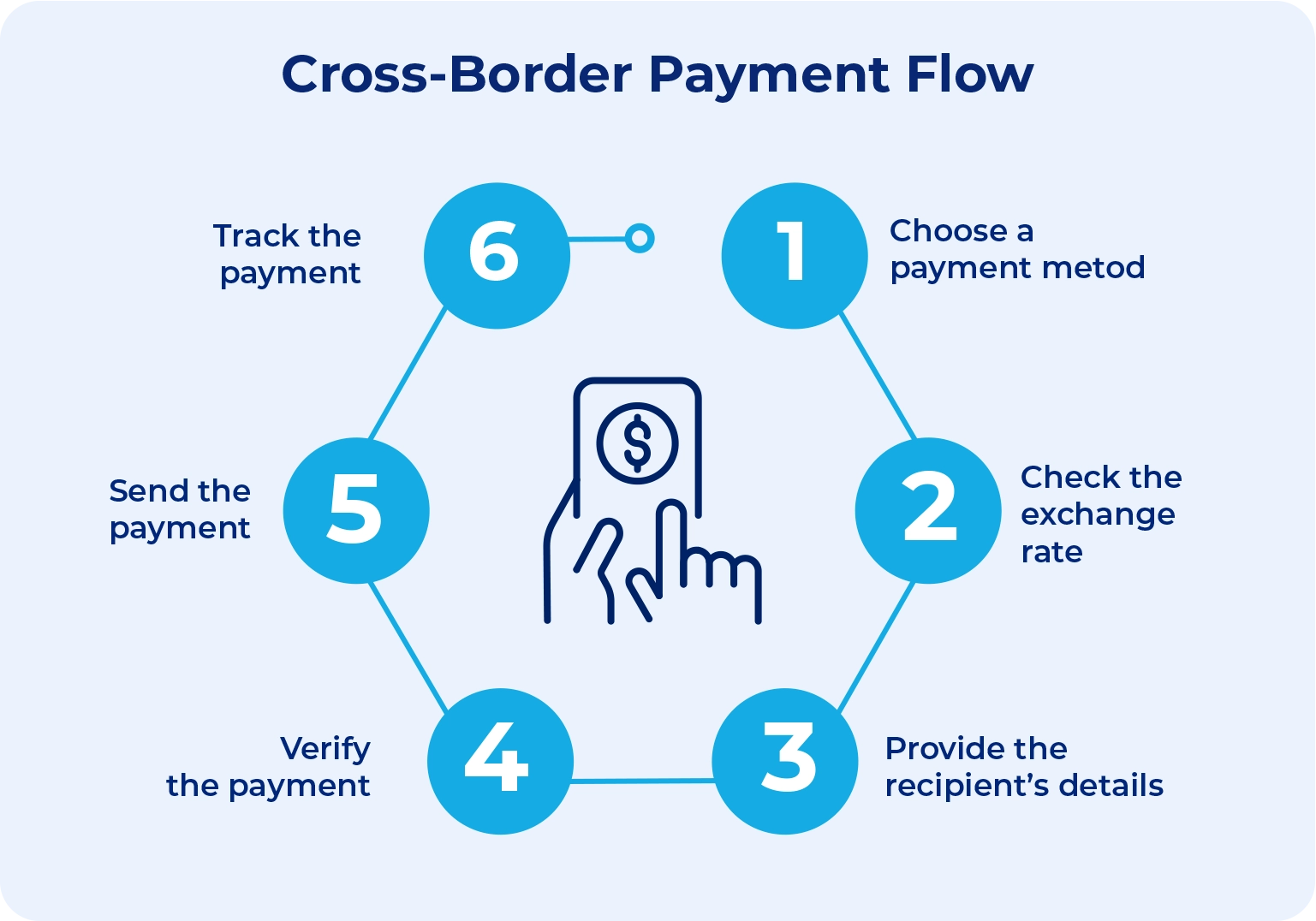
Source: decentro.tech
Types of cross-border payment systems
Cross-border payments come in various forms, each serving different needs in the global economy. From traditional bank transfers to modern digital wallets, the methods of moving money internationally continue to evolve. Cross border payments include:
Traditional methods
Bank Transfers (SWIFT & SEPA)
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT) and the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) are among the most common cross-border payment methods. These systems ensure a secure and dependable international network for the growing volume of financial transfers. SWIFT enables global transfers, while SEPA is commonly used in the European Union for euro transactions.
The main difference between SWIFT and SEPA is their geographical reach. SWIFT allows international users to transfer funds in multiple currencies across the world. SEPA is used only for Euro transfers within SEPA member countries.
SWIFT connects banks worldwide, making it ideal for global payments, while SEPA provides fast, low-cost transfers within the EU, especially for euro transactions. Each one has certain downsides, however. SWIFT can be expensive and slow, especially for smaller amounts and SEPA is limited to euro payments within the EU.
Credit & Debit Cards
They provide a simple way to pay for goods and withdraw cash in other countries. Payments go through global networks such as Visa, Mastercard, and American Express. When a person uses a card abroad, the amount is converted into their home currency and the exchange rate depends on the card issuer.
One main advantage of credit and debit cards is their ease of use. They work at millions of stores worldwide, which makes them a great choice for travelers and online shoppers. Credit cards also come with extra benefits. These include fraud protection, chargeback options, and travel rewards.
There are also some downsides. Many banks and card issuers add foreign transaction fees. These fees increase the total cost of purchases. Exchange rates may also have markups, making items more expensive. Credit and debit cards are a convenient across border payment option but users should check for fees and other limitations before using them internationally.
Bank Drafts
A bank draft is a safe way to make cross-border payments. It is a check that a bank issues for a customer and guarantees that the payment will be made. The customer buys the draft from their bank, which then gives them a document that is payable to the recipient.
The recipient can deposit the draft into their own account. The recipient’s bank will then process the payment. The bank guarantees the funds, so there is no risk of the draft bouncing. This makes bank drafts a reliable option for large international payments.
However, there are some disadvantages here too. Bank drafts can take time to process, and both the sender and recipient may have to pay fees. If the draft is lost or stolen, it can be hard to replace. Although bank drafts are a secure way to transfer money internationally, they are not always the fastest or most affordable option.
Modern solutions
Digital Wallets & FinTech Platforms (e.g., PayPal, Wise, Alipay)
These platforms allow fast and often cheaper cross-border payments with more convenient interfaces than traditional banking systems. Digital wallets and FinTech platforms like PayPal, Wise, and Alipay let users send and receive money anywhere in the world with a few clicks on a mobile app or computer.
One big advantage of digital wallets and FinTech platforms is their convenience. Users can send money to nearly any country without visiting a bank. These platforms also provide secure payment methods with encryption and fraud protection.
However, there are certain downsides to these modern solutions. Not all businesses or countries accept digital wallets and FinTech services. There may also be fees for currency exchange or withdrawing money to a bank account.
Cryptocurrency & Blockchain Payments
Cryptocurrency and blockchain are among the newest cross-border payment methods. Bitcoin and Ethereum run on decentralized networks not controlled by banks. Blockchain, the technology behind them, ensures secure, transparent, and unchangeable transactions.
One big benefit of using cryptocurrencies is the low transaction fees. Since they do not involve banks or financial institutions, fewer fees are applied. These payments can be completed quickly without intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies also offer more security through encryption and decentralized verification.
However, cryptocurrencies are known to be volatile. Not every business or country accepts cryptocurrency payments. Additionally, as the technology is developing, there is still regulatory uncertainty that creates challenges for both users and businesses.
Local Banking Solutions & Regional Payment Networks
Local banking solutions and regional payment networks are becoming more popular for cross-border payments. These systems work within specific regions or countries and depend on local banking infrastructure.
For instance, the Faster Payments Service (FPS) in the UK and the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) in Asia make fast and secure international transfers possible within certain areas. They are often quicker than traditional global methods.
One benefit of using local banking and regional payment networks is their lower cost. They typically charge lower fees than global systems like SWIFT. They are also more efficient for transfers between neighboring countries or regions with similar currencies and financial systems.
Yet, these networks may not work well for transactions outside their region. They may also offer less security and protection compared to global networks.
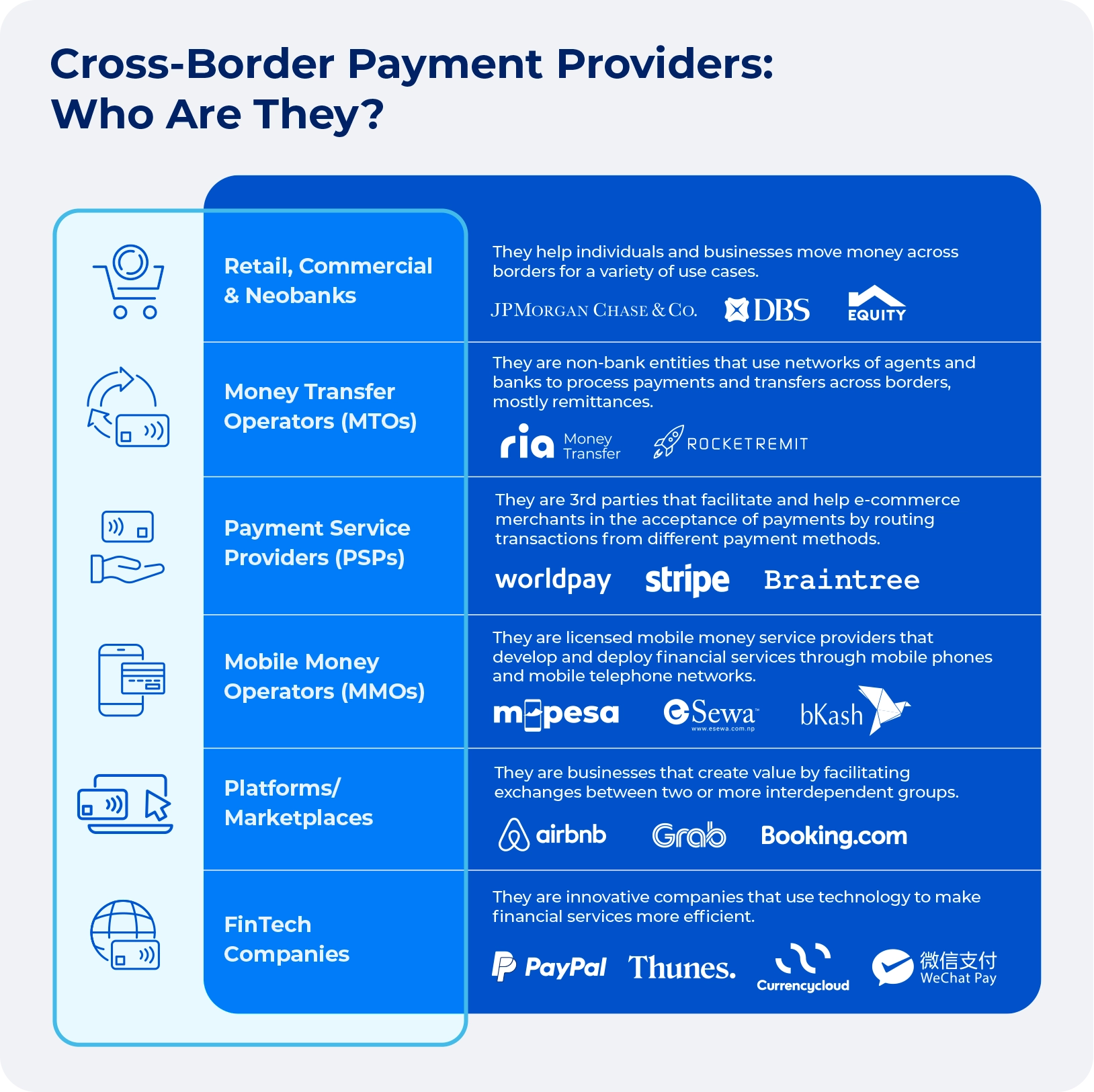
Source: thunes.com
Challenges in cross-border payments
There are four main challenges related to cross-border payments. These are high costs, slow speed, volatility risks and transparency issues. To address these and other challenges, ongoing collaboration between the private and public sectors is essential.
High transaction costs
Transfers often come with multiple fees. These include charges from the sending bank, intermediary banks, and the receiving bank. Additionally, banks and payment providers often apply poor exchange rates, which adds to the cost.
Another problem is the lack of clear pricing upfront. In many cases, the total cost of a transfer is not known from the start, which leads to unexpected charges.
Slow processing times
Traditional payment systems take several days to complete transfers. This is because they involve multiple intermediaries like banks and payment processors. The delay can be frustrating for businesses and individuals who need quick access to funds.
Time zones and different banking hours across countries can also make the process slower. New technologies like blockchain speed things up, but many transactions still rely on older systems.
Currency exchange & volatility risks
The thing with exchange rates is that they are always shifting, so you could end up with surprise costs. You might send money in one currency, but when it’s converted, it could be worth a lot less than you expected. This becomes a bigger issue when dealing with currencies that change fast.
For businesses and individuals making international transfers, it’s tough to predict how much it will actually cost. The unpredictability of exchange rates makes it a real challenge to plan payments, which only drives up costs and adds even more risks to international transactions.
Lack of transparency
In cross-border payments, hidden fees often appear during or after a transaction. Banks and payment providers don’t always provide a clear breakdown of these fees. This makes comparing services difficult. Without clear information, users may end up paying more and facing delays.
Best practices for businesses handling cross-border payments
Choosing the right payment provider
When managing cross-border payments, businesses need to select the right payment provider. Important factors to consider are cost, since fees can differ widely, speed, as fast transactions are necessary, and security, to protect transfers. Global coverage helps reach international markets, while regulatory compliance ensures that the business meets legal requirements in various countries.
Optimizing payment workflows
Automating payments helps speed up the process and reduces errors. It also ensures they are accurate and timely. It makes managing international transactions simpler and more efficient. By doing so, businesses save time and resources, making the entire process more reliable and cost-effective.
Foreign exchange (FX) risk management
To manage foreign exchange (FX) risks in cross-border payments, businesses can use strategies to protect against currency changes. They might choose forward contracts or options to lock in exchange rates. Another option is using multi-currency accounts. As the name suggests, these accounts allow businesses to hold and pay in different currencies. This helps lower FX risk and reduce fees.
Ensuring compliance with global regulations
Businesses should keep up with changing financial laws and AML rules. This will ensure compliance with global regulations. Partnering with payment providers who handle compliance efficiently can help. In this way, they can avoid penalties.
Key trends and innovations in cross-border payments in 2025
Blockchain & cryptocurrency solutions
In 2025, decentralized finance (DeFi) is helping make cross-border payments cheaper and faster. By removing intermediaries, DeFi improves the speed of transactions. Stablecoins, like USDT and USDC, are also becoming more widely used for instant payments. These stablecoins provide a secure option for faster payments across borders. Together, these trends are changing the way international payments work.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in payments
In 2025, AI will help detect fraud and assess risk in cross-border payments. It will improve security by identifying fraud quickly. Machine learning will also help route payments more efficiently. This will speed up transactions and reduce costs. On the whole, these technologies will make international payments safer and more efficient.
Real-Time Payments (RTP) & Instant Settlements
In 2025, real-time payments (RTP) and instant settlements will transform cross-border transactions. Payment networks offering real-time transfers will expand, making global payments faster. SWIFT GPI (Global Payments Innovation) will continue to grow, offering quicker and more transparent payments. Alternative solutions will also emerge, further enhancing efficiency and reducing delays in cross-border payment processing.
ISO 20022 Messaging Standard Adoption
More and more financial institutions are adopting ISO 20022 to improve cross-border payments. The system will create a common format for sharing payment details and help make transactions more transparent. Errors will decrease and processing will become more efficient. As adoption grows, international payments will be faster, more reliable, and easier to manage.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could change cross-border payments in 2025 by making transactions faster and more affordable. These government-backed digital currencies are also expected to improve security and reduce reliance on traditional banks. With more countries adopting CBDCs, international payments are likely to become more efficient. This shift will lower costs and simplify global transactions by reducing the need for intermediaries.

Source: uplabs.com
Future outlook: What’s next for cross-border payments?
FinTech and Big Tech companies will play an important role in shaping the future of cross-border payments. Players like Stripe, Payoneer, and Revolut are making payments faster, cheaper, and more flexible by avoiding traditional banks. These companies are growing in popularity because they are transparent and efficient.
Big Tech companies like Apple, Google, and Amazon also play a key role in cross-border payments thanks to their global reach and technical expertise. As both FinTech and Big Tech keep innovating, cross-border payments will become faster and easier for people around the world.
Financial companies must stay updated on real-time payments, digital currencies, and AI solutions. They need to adjust their strategies to make transactions smoother and more affordable as improving payment strategies will be crucial for success in 2025 and beyond.



